Note
Go to the end to download the full example code
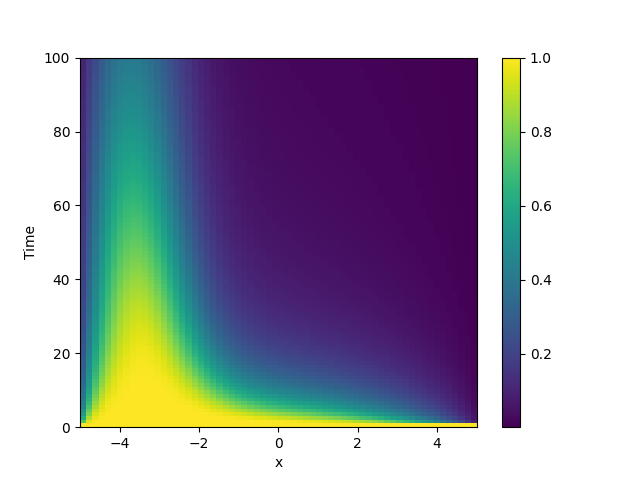
2.16. Diffusion equation with spatial dependence
This example solve the Diffusion equation with a heterogeneous diffusivity:
\[\partial_t c = \nabla\bigr( D(\boldsymbol r) \nabla c \bigr)\]
using the PDE class. In particular, we consider
\(D(x) = 1.01 + \tanh(x)\), which gives a low diffusivity on the left side of the
domain.
Note that the naive implementation,
PDE({"c": "divergence((1.01 + tanh(x)) * gradient(c))"}), has numerical
instabilities. This is because two finite difference approximations are nested. To
arrive at a more stable numerical scheme, it is advisable to expand the divergence,
\[\partial_t c = D \nabla^2 c + \nabla D . \nabla c\]
/home/docs/checkouts/readthedocs.org/user_builds/py-pde/checkouts/0.30.0/pde/grids/boundaries/local.py:1822: NumbaDeprecationWarning: The 'nopython' keyword argument was not supplied to the 'numba.jit' decorator. The implicit default value for this argument is currently False, but it will be changed to True in Numba 0.59.0. See https://numba.readthedocs.io/en/stable/reference/deprecation.html#deprecation-of-object-mode-fall-back-behaviour-when-using-jit for details.
def virtual_point(
from pde import PDE, CartesianGrid, MemoryStorage, ScalarField, plot_kymograph
# Expanded definition of the PDE
diffusivity = "1.01 + tanh(x)"
term_1 = f"({diffusivity}) * laplace(c)"
term_2 = f"dot(gradient({diffusivity}), gradient(c))"
eq = PDE({"c": f"{term_1} + {term_2}"}, bc={"value": 0})
grid = CartesianGrid([[-5, 5]], 64) # generate grid
field = ScalarField(grid, 1) # generate initial condition
storage = MemoryStorage() # store intermediate information of the simulation
res = eq.solve(field, 100, dt=1e-3, tracker=storage.tracker(1)) # solve the PDE
plot_kymograph(storage) # visualize the result in a space-time plot
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 13.686 seconds)