Note
Go to the end to download the full example code
2.5. Simple diffusion equation
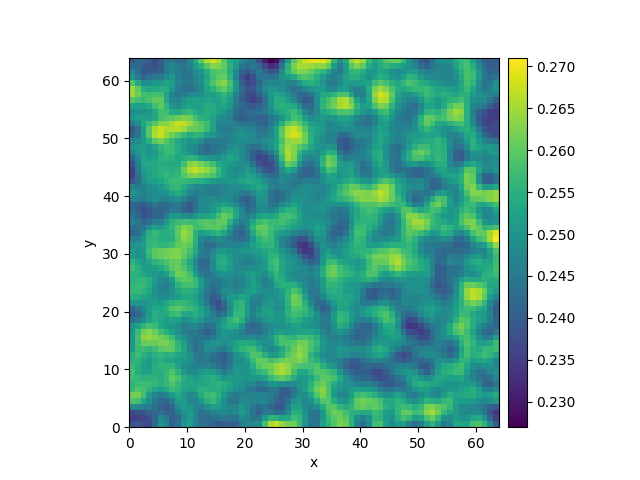
This example solves a simple diffusion equation in two dimensions.
0%| | 0/10.0 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
Initializing: 0%| | 0/10.0 [00:00<?, ?it/s]/home/docs/checkouts/readthedocs.org/user_builds/py-pde/checkouts/0.30.1/pde/grids/boundaries/local.py:1822: NumbaDeprecationWarning: The 'nopython' keyword argument was not supplied to the 'numba.jit' decorator. The implicit default value for this argument is currently False, but it will be changed to True in Numba 0.59.0. See https://numba.readthedocs.io/en/stable/reference/deprecation.html#deprecation-of-object-mode-fall-back-behaviour-when-using-jit for details.
def virtual_point(
0%| | 0/10.0 [00:10<?, ?it/s]
0%| | 0.00316/10.0 [00:10<9:21:02, 3367.34s/it]
1%| | 0.06596/10.0 [00:10<26:43, 161.40s/it]
10%|9 | 0.96267/10.0 [00:10<01:39, 11.06s/it]
10%|9 | 0.96267/10.0 [00:10<01:40, 11.07s/it]
100%|##########| 10.0/10.0 [00:10<00:00, 1.07s/it]
100%|##########| 10.0/10.0 [00:10<00:00, 1.07s/it]
from pde import DiffusionPDE, ScalarField, UnitGrid
grid = UnitGrid([64, 64]) # generate grid
state = ScalarField.random_uniform(grid, 0.2, 0.3) # generate initial condition
eq = DiffusionPDE(diffusivity=0.1) # define the pde
result = eq.solve(state, t_range=10)
result.plot()
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 10.904 seconds)