Note
Click here to download the full example code
2.11. Setting boundary conditions¶
This example shows how different boundary conditions can be specified.
Out:
0%| | 0/10.0 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
Initializing: 0%| | 0/10.0 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
0%| | 0/10.0 [00:07<?, ?it/s]
0%| | 0.005/10.0 [00:08<4:31:39, 1630.76s/it]
0%| | 0.01/10.0 [00:09<2:31:54, 912.35s/it]
0%| | 0.015/10.0 [00:09<1:41:13, 608.26s/it]
2%|2 | 0.25/10.0 [00:09<05:55, 36.50s/it]
2%|2 | 0.25/10.0 [00:09<05:56, 36.55s/it]
100%|##########| 10.0/10.0 [00:09<00:00, 1.09it/s]
100%|##########| 10.0/10.0 [00:09<00:00, 1.09it/s]
from pde import DiffusionPDE, ScalarField, UnitGrid
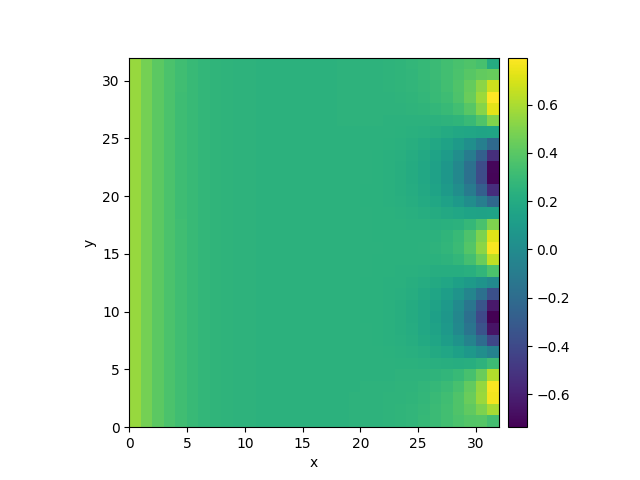
grid = UnitGrid([32, 32], periodic=[False, True]) # generate grid
state = ScalarField.random_uniform(grid, 0.2, 0.3) # generate initial condition
# set boundary conditions `bc` for all axes
bc_x_left = {"derivative": 0.1}
bc_x_right = {"value": "sin(y / 2)"}
bc_x = [bc_x_left, bc_x_right]
bc_y = "periodic"
eq = DiffusionPDE(bc=[bc_x, bc_y])
result = eq.solve(state, t_range=10, dt=0.005)
result.plot()
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 9.293 seconds)