Note
Go to the end to download the full example code
2.21 1D problem - Using custom class
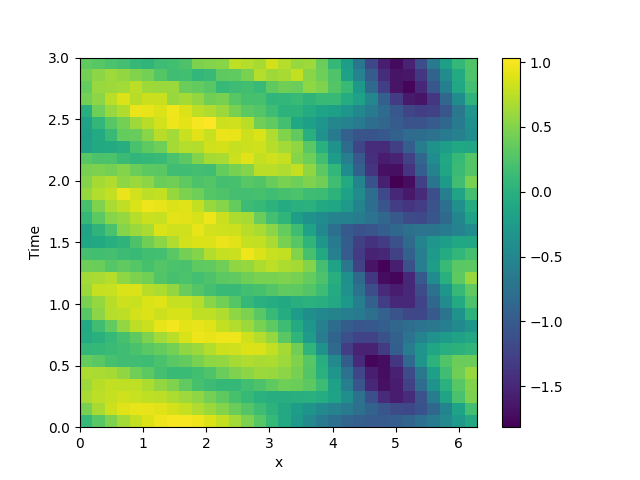
This example implements a PDE that is only defined in one dimension. Here, we chose the Korteweg-de Vries equation, given by
\[\partial_t \phi = 6 \phi \partial_x \phi - \partial_x^3 \phi\]
which we implement using a custom PDE class below.
from math import pi
from pde import CartesianGrid, MemoryStorage, PDEBase, ScalarField, plot_kymograph
class KortewegDeVriesPDE(PDEBase):
"""Korteweg-de Vries equation"""
def evolution_rate(self, state, t=0):
"""implement the python version of the evolution equation"""
assert state.grid.dim == 1 # ensure the state is one-dimensional
grad_x = state.gradient("auto_periodic_neumann")[0]
return 6 * state * grad_x - grad_x.laplace("auto_periodic_neumann")
# initialize the equation and the space
grid = CartesianGrid([[0, 2 * pi]], [32], periodic=True)
state = ScalarField.from_expression(grid, "sin(x)")
# solve the equation and store the trajectory
storage = MemoryStorage()
eq = KortewegDeVriesPDE()
eq.solve(state, t_range=3, solver="scipy", tracker=storage.tracker(0.1))
# plot the trajectory as a space-time plot
plot_kymograph(storage)
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 2.201 seconds)